Visit and Join the WeHeal WeHeal Hepatitis Community.
For more information, see: Mayoclinic.gov | Wikipedia
Visit and Join the WeHeal WeHeal Hepatitis Community.
For more information, see: Mayoclinic.gov | Wikipedia

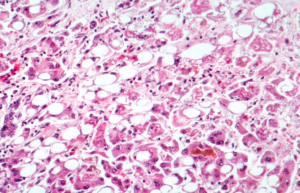
Hepatitis (plural: hepatitides) is a medical condition defined by the inflammation of the liver and characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells in the tissue of the organ. Hepatitis may occur with limited or no symptoms, but often leads to jaundice (a yellow discoloration of the skin, mucous membrane, and conjunctiva), poor appetite, and malaise. This disease is acute when it lasts less than six months and chronic when it persists longer.
It can be self-limiting (healing on its own), can progress to chronic hepatitis, or, rarely, can cause acute liver failure. This disease may have no symptoms, or may progress over time to fibrosis (scarring of the liver) and cirrhosis (chronic liver failure). Cirrhosis of the liver increases the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma (a form of liver cancer.
Worldwide, viral hepatitis is the most common cause of liver inflammation. Other causes include autoimmune diseases and ingestion of toxic substances (notably alcohol), certain medications (such as paracetamol), some industrial organic solvents, and plants.
The term is derived from the Greek hêpar (ἧπαρ), meaning “liver”, and the suffix -itis (-ῖτις), meaning “inflammation”.
Visit and Join the WeHeal WeHeal Hepatitis Community.
For more information, see: Mayoclinic.gov | Wikipedia
WeHeal is very grateful to our valued sources of information which include Wikipedia, WebMD, ClinicalTrials.gov, Cancer.gov, Infoplease, and the US CDC (Center for Disease Control).