Visit and Join the WeHeal Back Pain Community.
For more information, see: Mayo Clinic | Wikipedia
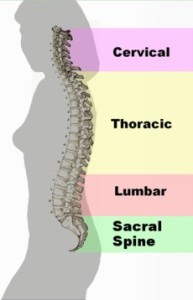
Back pain is pain felt in the back that usually originates from the muscles, nerves, bones, joints or other structures in the spine. However, internal structures such as the gallbladder and pancreas may also refer pain to the back.
Most back pain is felt in the lower back. The remainder of this article considers back pain in all regions.
The onset of back pain may be acute or chronic. It can be constant or intermittent, stay in one place or radiate to other areas. It may be characterised by a dull ache, or a sharp or piercing or burning sensation. The pain may radiate into the arms and hands as well as the legs or feet, and may include symptoms other than pain. Examples of these symptoms may include tingling, weakness or numbness in the legs and arms, indicating injury to the nerves.
Although back pain is common, it is rare for it to be permanently disabling. Even in most cases of disc herniations and stenosis, whether you do nothing, whether you get a shot or whether you have surgery, after one year, results are nearly the same with general resolution of pain. In the U.S., acute low back pain (also called lumbago) is the fifth most common reason for physician visits. About nine out of ten adults experience back pain at some point in their life, and five out of ten working adults have back pain every year. Low back pain causes 40% of missed days of work in the United States. Additionally, it is the single leading cause of disability worldwide.
Back pain may be classified by various methods to aid its diagnosis and management. The anatomic classification of back pain follows the segments of the spine: cervical, thoracic, lumbar or sacral.
The duration of back pain is considered in three categories, following the expected pattern of healing of connective tissue. Acute pain lasts up to 12 weeks, subacute pain refers to the second half of the acute period (6 to 12 weeks), and chronic pain is pain which persists beyond 12 weeks.
The character of back pain indicates its likely tissue of origin. Nonspecific back pain is believed to be due from the soft tissues such as muscles, fascia, and ligaments.[5] Radicular pain with or without spinal stenosis indicates involvement of nervous tissue. Secondary back pain results from a known medical diagnosis such as infection or cancer. Non specific pain indicates that the cause is not known precisely but is believed to be due from the soft tissues such as muscles, fascia, and ligaments.
Back pain has several causes. Approximately 98 percent of back pain patients are diagnosed with nonspecific acute back pain in which no serious underlying pathology is identified. Nearly 2 percent are comprised by metastatic cancers, while serious infections such as spinal osteomyelitis and epidural abscesses account for fewer than 1 percent. The most common cause of neurologic impairment including weakness or numbness results from a herniated disc. Nearly 95 percent of disc herniations occur at the lowest two lumbar intervertebral levels.
Visit and Join the WeHeal Back Pain Community.
For more information, see: Mayo Clinic | Wikipedia
WeHeal is very grateful to our valued sources of information which include Wikipedia, WebMD, ClinicalTrials.gov, Cancer.gov, Infoplease, and the US CDC (Center for Disease Control).