Visit and Join the WeHeal Seasonal Affective Disorder
Information and References: WebMd | Wikipedia | Mayo Clinic
Clinical Trials: Clinicaltrials.gov | In Clinical Trials | EU Clinical Trials Register | WeHeal Guide to Researching Clinical Trials
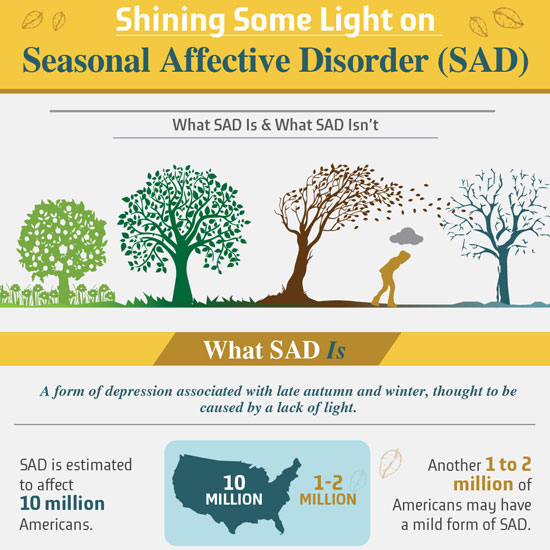
Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) is a type of depression that tends to occur (and recur) as the days grow shorter in the fall and winter. It is believed that affected people react adversely to the decreasing amounts of sunlight and the colder temperatures as the fall and winter progress. It is important to note that although seasonal affective disorder usually presents in the fall and winter there are those who suffer from this condition during the summer instead of, or in addition to, during the fall or winter.
Seasonal affective disorder has not been long recognized as an official diagnosis. The term first appeared in print in 1985. Seasonal affective disorder is also sometimes called winter depression, winter blues, or the hibernation reaction.
The incidence of seasonal affective disorder increases in people who are living farther away from the equator. Statistics on seasonal affective disorder in the United States include that this disorder occurs in 1% to 10% of adults, and its prevalance is dependent on geographical location. Seasonal affective disorder is less common where there is snow on the ground. Seasonal affective disorder is about four times more common in women than men, and the average age of people when they first develop this illness is 23 years of age. People of all ages can develop seasonal affective disorder.
Patient Resources and Related Organizations: The Seasonal Affective Disorder Association
News and Media: News-Medical.net | NIH
Visit and Join the WeHeal Seasonal Affective Disorder
WeHeal is very grateful to our valued sources of information which include Wikipedia, WebMD, ClinicalTrials.gov, Cancer.gov, Infoplease, and the US CDC (Center for Disease Control).